2 – Benefits of Choosing Cotton
3 – Cotton vs Other Fabrics
4 – How Cotton Is Manufactured
5 – Common Uses in Fashion
6 – Understanding the Environmental Impact of Cotton
7 – Exploring Price Points and Value for Money
8 – Conclusion
9 – FAQs
What is Cotton?
Cotton is one of the most widely used natural fibers in the world, renowned for its softness, breathability, and versatility. At its core, cotton is a plant-based fiber that grows around the seeds of the cotton plant (Gossypium species). This fluffy, white fiber has been harvested and used by civilizations for thousands of years, from the ancient Egyptians to today’s global textile industry. But cotton is more than just the fabric we find in our shirts or bed linens—it is a raw material that combines nature’s engineering with human innovation.
Here’s what makes cotton unique:
- Natural origin: Cotton comes from the seed hairs of the cotton plant, cultivated mainly in warm climates such as the United States, India, China, and parts of Africa. The fibers are spun into yarn or thread and then woven or knitted into fabric.
- Renewable and biodegradable: As a natural fiber, cotton is both renewable (it can be replanted seasonally) and biodegradable, meaning it breaks down naturally at the end of its life cycle without harming the environment.
- Everyday use: From lightweight T-shirts and durable denim jeans to soft towels and medical bandages, cotton’s applications are endless due to its comfort, durability, and moisture-absorbing properties.

Benefits of Choosing Cotton
Choosing cotton offers a range of benefits that make it a preferred fabric for clothing, home textiles, and even specialized industrial uses. Its natural qualities and versatility have made it a staple for centuries, and modern consumers continue to value cotton for both comfort and performance. Key benefits include:
- Softness and comfort: Cotton fibers are naturally soft, making cotton fabric gentle against the skin. This is why it’s often chosen for baby clothes, underwear, and bedding where comfort matters most.
- Breathability: Cotton fabric allows air to flow through it easily, helping to regulate body temperature and keep the wearer cool in warm weather. This makes it an ideal choice for summer clothing and sportswear.
- Moisture absorption: Cotton can absorb up to 27 times its weight in water, efficiently wicking away sweat and keeping you dry and comfortable. This property is especially valued in towels, socks, and activewear.
- Hypoallergenic properties: Cotton is less likely to cause allergic reactions or skin irritation, making it suitable for people with sensitive skin or allergies.
- Durability and easy care: High-quality cotton is strong and hard-wearing. It can endure frequent washing and use without losing its shape or softness, and it’s easy to care for at home—usually machine-washable and resistant to pilling.
- Sustainability: As a natural and biodegradable fiber, cotton has an advantage over synthetic alternatives in terms of environmental impact, particularly when grown and processed responsibly.
- Versatility: From fine cotton used in delicate blouses to heavy cotton used in denim or canvas, cotton adapts to a wide range of products and styles.
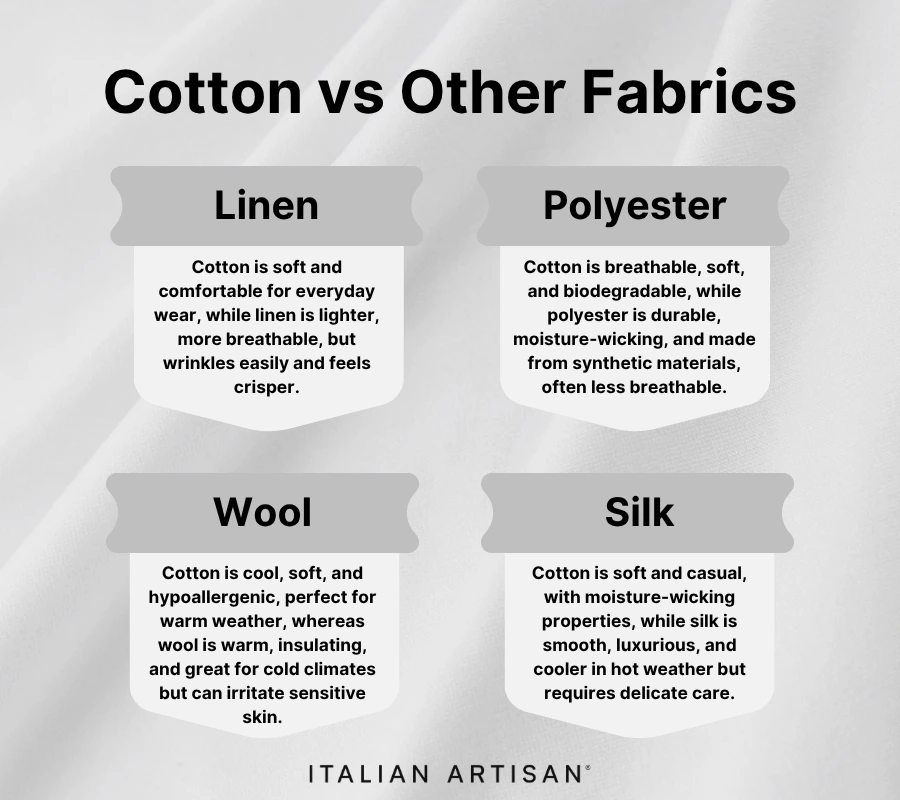
Cotton vs Other Fabrics
When choosing fabrics, it’s essential to understand how cotton compares to other popular materials like polyester, wool, linen, and silk. While each fabric has its unique qualities, cotton stands out due to its natural origin, comfort, and versatility. Here’s a breakdown of how cotton compares to other commonly used fabrics:
- Cotton vs Polyester:
Polyester is a synthetic fabric made from petroleum-based products, while cotton is a natural fiber.- Breathability: Cotton allows better airflow, making it cooler and more breathable compared to polyester, which can trap heat and moisture.
- Durability: Polyester is highly durable and resistant to wrinkles, but it lacks the softness and comfort that cotton offers.
- Environmental Impact: Cotton, when sustainably sourced, is biodegradable, while polyester contributes to microplastic pollution and takes centuries to decompose.
- Cotton vs Linen:
Linen, made from the flax plant, is another natural fabric, often compared to cotton for its lightness and breathability.- Texture: Linen is known for its crisp texture and tends to wrinkle more than cotton, which has a smoother finish.
- Moisture Absorption: Both fabrics are highly absorbent, but cotton tends to retain moisture longer than linen, which dries more quickly.
- Durability: Linen is generally stronger than cotton but can be more delicate when wet, while cotton is softer and can withstand frequent washing.
- Cotton vs Wool:
Wool is derived from animal fibers, such as sheep, and is often used for colder weather clothing.- Temperature Regulation: Wool is an excellent insulator, keeping warmth in during winter, while cotton is better suited for warmer climates due to its cooling properties.
- Skin Sensitivity: Cotton is gentler on the skin, while wool can cause irritation in some individuals due to its coarse texture.
- Care and Maintenance: Wool requires more delicate care, often needing hand washing or dry cleaning, whereas cotton is easy to care for and more durable in the long run.
- Cotton vs Silk:
Silk is a luxurious fabric made from the fibers of silkworms, known for its smooth texture and high sheen.- Softness and Feel: While both cotton and silk are soft, silk has a shinier, more luxurious feel, while cotton remains more matte and casual.
- Breathability: Both fabrics are breathable, but cotton is often more comfortable in hot and humid weather, while silk tends to be warmer in cooler conditions.
- Cost: Silk is significantly more expensive than cotton due to its labor-intensive production process and premium qualities.
How Cotton Is Manufactured
The journey of cotton from plant to fabric is a complex and multi-step process that transforms raw cotton into the versatile fabric used in fashion. Understanding this process helps appreciate the value and craftsmanship that goes into cotton-based clothing. Here’s how cotton is typically manufactured, from cultivation to finished garment:
- Cotton Harvesting: Cotton is harvested from the cotton plant, typically in warm climates. This can be done manually or with machines, depending on the region and technology available.
- Ginning: After harvesting, cotton goes through a cotton gin, which separates the fibers from the seeds. This step is crucial for ensuring only the cotton fibers are used for fabric production.3
- Spinning: The cotton fibers are then spun into yarn. Spinning machines twist the fibers into strands, creating different yarn types based on thickness and texture for various fabric uses.
- Weaving or Knitting: Once the yarn is ready, it is either woven or knitted into fabric. Weaving involves interlacing two sets of yarn—one running horizontally (weft) and the other vertically (warp)—to create a stable and durable fabric. Knitting, on the other hand, involves looping the yarn to form a stretchy fabric often used in garments like t-shirts and sweaters.
- Woven cotton fabrics tend to be stronger and more structured, making them ideal for items like shirts, trousers, and outerwear.
- Knitted cotton fabrics are more flexible and breathable, often used for casual wear and undergarments.
- Dyeing and Printing: Once the fabric is formed, it’s dyed or printed. Dyeing changes the fabric’s color, while printing applies patterns or designs. Both processes can be done using natural or synthetic methods, depending on the desired outcome.
- Finishing: After dyeing or printing, cotton fabric goes through a series of finishing processes to enhance its look, feel, and durability. This may include:
- Brushing: A process that makes cotton fabric softer and more velvety to the touch.
- Pre-shrinking: Ensures the fabric won’t shrink excessively after washing.
- Softening: To make the fabric smoother and more comfortable.
- Water-repellent treatments: Applied for functional clothing like jackets or outdoor wear.
- Garment Manufacturing: Once the fabric is finished, it is ready to be turned into garments. This involves cutting the fabric into the necessary patterns, stitching the pieces together, and adding finishing touches like buttons, zippers, and labels. The garment is then pressed, packaged, and shipped.

Produce your fashion collection with us
Common Uses in Fashion
Cotton is one of the most versatile fibers in the fashion industry, used in a wide range of garments and accessories. Thanks to its comfort, durability, and breathability, cotton plays a key role in both everyday fashion and high-end collections. Here are some of the most common uses of cotton in fashion:
- T-Shirts and Casual Wear: Cotton is a go-to fabric for t-shirts, casual shirts, and sweatshirts due to its soft texture, breathability, and comfort. Cotton’s ability to absorb moisture makes it ideal for warm weather, ensuring that it feels cool and light against the skin.
- Jeans and Denim: Cotton is the primary material used to make denim, the fabric that defines jeans. Denim’s strength and durability come from cotton’s long fibers, making it the perfect choice for rugged, everyday wear. Cotton denim is also easily dyed, allowing for various washes and finishes that suit different styles.
- Underwear and Lingerie: Because cotton is soft, breathable, and hypoallergenic, it is commonly used in underwear, bras, and other lingerie items. It helps maintain comfort throughout the day and is gentle on the skin, making it ideal for intimate wear.
- Dresses and Blouses: Lightweight cotton fabrics like poplin and voile are frequently used in summer dresses, blouses, and shirts. These fabrics are breathable, making them perfect for warmer climates, and they hold their shape well after washing.
- Activewear: Cotton is also used in some types of activewear, particularly for light exercise or casual athletic wear. While synthetic fabrics like polyester dominate in performance gear, cotton is favored for its softness, moisture-wicking ability, and comfort during low-intensity activities.
- Socks: Cotton socks are a staple in everyday wardrobes due to their comfort and moisture-absorbing qualities. Cotton is often blended with synthetic fibers like spandex for added stretch and durability, creating socks that are comfortable and long-lasting.
- Outerwear: Cotton can also be found in outerwear like jackets and coats, particularly those made from thicker, durable fabrics such as canvas or twill. These cotton fabrics offer a soft, breathable alternative to heavier materials, providing comfort and versatility in different climates.
- Handbags and Accessories: Cotton canvas is often used for making durable yet lightweight handbags, totes, and backpacks. It offers a stylish and eco-friendly option for fashion accessories and is easily customizable with prints and embroidery.

Understanding the Environmental Impact of Cotton
While cotton is a natural and biodegradable fiber, its environmental impact can be significant, particularly during its cultivation and processing stages. Here are the key environmental concerns:
- Water Usage: Cotton farming requires a large amount of water—about 2,700 liters to produce enough cotton for a single t-shirt. This contributes to water scarcity, especially in regions already facing water stress.
- Chemical Use: Traditional cotton farming relies heavily on pesticides and fertilizers, which can pollute the environment, harm wildlife, and contaminate water sources. Cotton farming is one of the largest users of agricultural chemicals.
- Soil Degradation: Intensive cotton farming can lead to soil erosion and loss of nutrients, requiring more chemical inputs and compromising the land’s long-term fertility.
- Processing Impact: Cotton processing, including spinning, dyeing, and finishing, requires energy and water, contributing to carbon emissions and environmental pollution, especially through the dyeing process.
- Waste: Cotton-based garments often end up in landfills, where they can take years to decompose. This adds to textile waste, a major issue in the fashion industry.
- Sustainable Solutions: To reduce cotton’s environmental impact, alternatives like organic cotton, water-saving technologies, and recycled cotton are becoming more common. These methods help conserve resources and reduce waste.

Exploring Price Points and Value for Money
When it comes to cotton-based products, the price can vary significantly based on factors such as quality, production methods, and brand positioning. Understanding the price points and what contributes to the value for money is essential for both consumers and manufacturers in the fashion industry.
- Price Range of Cotton Products
- Budget Cotton: Affordable cotton items, often mass-produced, may use lower-quality cotton, resulting in shorter durability and lower comfort levels. These products are typically found in fast fashion brands and are priced to be accessible for everyday consumers.
- Mid-Range Cotton: Mid-range cotton products strike a balance between price and quality. These products often use higher-quality cotton, such as combed or carded cotton, and might incorporate sustainable practices like better dyeing processes or water-efficient production methods.
- Premium Cotton: Premium cotton items, such as those made from organic cotton or Egyptian cotton, are priced higher due to superior quality, more sustainable farming practices, and longer-lasting comfort. These products are often marketed as eco-friendly and luxurious, justifying their higher cost.
- Factors Influencing Price
- Cotton Quality: The finer and longer the cotton fibers, the more expensive the product. Higher-quality cotton is softer, more durable, and more comfortable against the skin, which adds value to the product.
- Production Practices: Ethical and sustainable practices, like organic farming, fair wages, and eco-friendly dyeing, contribute to higher production costs but add value in terms of environmental impact and worker conditions.
- Branding: Luxury brands or companies with strong reputations often charge a premium for cotton products due to their design, craftsmanship, and brand value, regardless of the raw material’s cost.
- Value for Money
- Cotton’s value for money depends on how well it meets the consumer’s needs. While budget options may save money upfront, mid-range and premium cotton products often offer longer-lasting quality, comfort, and sustainability. For consumers looking to invest in durable, high-quality garments, spending more on cotton can prove to be a better long-term investment. Additionally, supporting sustainable cotton production can contribute to environmental and ethical causes, which is increasingly becoming a priority for many shoppers.

Conclusion
Cotton remains one of the most versatile and widely used fabrics in the fashion industry, thanks to its natural origin, comfort, and adaptability. From its soft texture to its breathability and wide range of applications, cotton continues to play a vital role in everyday fashion, as well as in luxury and sustainable design. However, like any natural resource, cotton production comes with environmental challenges, including high water usage and chemical impact.
As consumers and manufacturers, it’s important to be mindful of these issues and make informed choices that support more sustainable practices, such as organic and recycled cotton. By understanding the various factors that affect cotton’s price, quality, and environmental footprint, we can contribute to a more responsible and thoughtful fashion industry. Ultimately, cotton’s enduring popularity reflects its unmatched combination of comfort, durability, and value for money, making it a staple in both our wardrobes and the global textile market.
FAQs
- What is cotton made from? Cotton is made from the fluffy fibers that grow around the seeds of the cotton plant (Gossypium species). These fibers are harvested, cleaned, and spun into yarn or thread, which is then woven or knitted to create fabric.
- Is cotton a natural or synthetic fabric? Cotton is a natural fabric. It comes from the cotton plant, making it biodegradable and renewable, unlike synthetic fabrics made from petroleum-based materials.
- Why is cotton so popular in fashion? Cotton is popular due to its softness, breathability, and comfort. It is durable, easy to care for, and suitable for various climates, making it ideal for everyday clothing and high-quality garments.
- Is cotton eco-friendly? Cotton can be eco-friendly when grown and processed sustainably. Organic cotton farming, which avoids synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, helps reduce environmental impacts. However, traditional cotton farming can consume significant water and involve chemical use, contributing to environmental challenges.
- How is cotton fabric made? Cotton fabric is made through several steps: First, cotton is harvested from the plant. Next, the fiber is separated from the seeds in a process called ginning. The fibers are then spun into yarn, which is either woven or knitted into fabric. Finally, the fabric is dyed and finished to achieve the desired color and texture.
- What are the different types of cotton fabric? There are various types of cotton fabric, each suited for different uses. Poplin is a smooth, lightweight fabric often used for shirts and blouses. Denim is a durable, woven fabric commonly used for jeans and jackets. Muslin is a lightweight, plain-woven fabric often used for summer clothing. Terrycloth, with its loops of yarn, is ideal for towels and bathrobes due to its absorbency.
- Is cotton good for sensitive skin? Yes, cotton is hypoallergenic and gentle on the skin. It’s commonly recommended for people with sensitive skin or allergies because it is less likely to cause irritation compared to synthetic fabrics.
- Can cotton be recycled? Yes, cotton can be recycled. Used cotton fabrics can be reprocessed into new yarns, which are then used to create new garments or textiles, reducing waste and the need for virgin cotton.
- How can I care for cotton clothing? Cotton clothing is generally easy to care for. You can machine wash cotton garments with mild detergent, although washing in cold water helps preserve color. Cotton may shrink slightly after washing, so it’s important to follow care labels for best results.
- Why is cotton so expensive sometimes?Cotton prices can vary depending on factors such as quality, production methods, and market demand. Organic cotton and high-quality cotton, such as Egyptian cotton, tend to be more expensive due to sustainable farming practices, better durability, and a more labor-intensive production process.






